Episode 043: Myeloma Series, Pt.4 - Myeloma Pharmacology
In this continuation of our myeloma series, we begin our discussion about treatment options for multiple myeloma, focusing first on pharmacology. We are so thrilled to have a special guest, Kathryn Maples, PharmD, BCOP who is a clinical pharmacy specialist in Multiple Myeloma at the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, Georgia!
Introduction
What is a “triplet regimen”?: Immunomodulatory agent (aka “IMID”, end in “-omide”)+Proteasome inhibitor (end in “-zomib”) + Steroid.
Common triplet regimen is VRD: Velcade (brand name for bortezomib), Revlimid (brand name for lenalidomide), and Dexamethasone.
What is a “auadruplet regimen”?: Triplet regimen + a CD38 antibody (most commonly daratumumab)
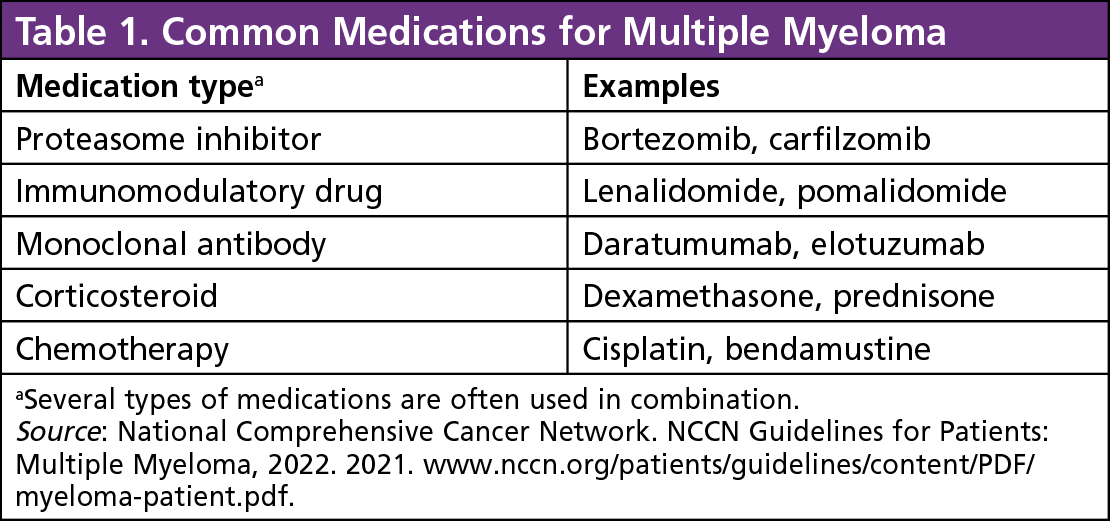
Common medications for multiple myeloma. (Image from Conquer-magazine.com; no copyright infrigement intended)
Bortezomib (Velcade)
What are the toxicities associated with bortezomib?
Peripheral Neuropathy is the major toxicity.
It cannot be prevented.
Most commonly occurs within the first five cycles.
Management: Dose modification may be required based on the grade of neuropathy. Neuropathic agents can be used for symptom control, including gabapentin, pregabalin, duoloxetine.
Other side effects of bortezomib include:
Herpes simplex/zoster reactivation, antiviral prophylaxis is required.
Diarrhea or constipation
Stye (treated with Doxycycline)
Drug interactions: It is inhibited by with Vitamin C (doses >500mg), green tea
Dose modification guideliens for bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy. (Image from Table 4 from Argyriou et al. Blood 2008. No copyright infringement intended)
Why do we use bortezomib in myeloma treatment?
Because of SWOG S0777 trial, which compared VRD vs RD
In patients with newly diagnosed myeloma, the addition of bortezomib to lenalidomide and dexamethasone resulted in significantly improved progression-free and overall survival and had an acceptable risk-benefit profile.
SWOG S0777 trial VRd protocol used twice-weekly intravenous bortezomib.
Twice weekly vs once weekly velcade:
Dose intensities are similar.
Neurotoxicity rates are lower with once-weekly subcutaneous bortezomib.
Although it is given as a Subcutaneous injection, it cannot be given at home.
Kathyrn states that deeper depths of response can be seen with twice weekly
Lenolidomide (Revlimid)
What is the mechanism of action of IMIDs?
IMIDs has multifactorial mechanism of action, including:
Direct cytotoxicity.
Anti-angiogenesis.
Enhanced immune properties (increasing Natural Killer cells, T-cells)
What are the toxicities of lenolidomide?
Rash
Can see more commonly during maintenance therapy since during induction, they are getting steroids as part of their treatment regimen
Treated with topical corticosteroids (usually); rarely needing oral steroids
Diarrhea:
Occurs due to bile acid malabsorption
Can be treated with bile acid sequestrants
Cytopenias:
May require dose reduction!
Growth factors may be required, especially in patients who have marrow infiltration with multiple myeloma and have baseline cytopenias
Unlike with other cancer treatments, G-CSF can be given on the same day as lenolidomide
During induction treatment, growth factors can be given 2-3 times weekly to avoid dose reductions
Fatigue: May also require dose reduction
Venous thromboembolic events (see below)
Should lenolidomide always be started with a max dose (25mg)?
An individualized discussion.
In elderly or frail patients with poorer performance status or renal impairment, consider starting at a lower dose, such as 10-15mg and escalate as tolerated
If patients are transplant eligible, have good performance status and renal function, consider starting at max dose
What is the REMS program for lenolidomide?
REMS (risk-evaluation and medication strategy) program is mandated for drugs by the FDA based on the safety of the drug.
Important notes for providers:
All females of childbearing age must undergo a pregnancy test before each refill
At least 2 forms of birth control, with one being a barrier method, are required, up until 4 weeks after discontinuing the drug
Patients must complete a survey before each refill
What are the recommendations regarding DVT prophylaxis in patients getting IMIDs?
Younger patients with few risk factors can be given 81 mg Aspirin daily.
Scoring systems like IMPEDE score and SAVED score are in NCCN guidelines can be used to determine the risk of VTE. In her practice, they use clinical scenarios, most notably any prior history of VTE (provoked or unprovoked), which would prompt her to do prophylactic anticoagulation.
Daratumumab (Darzalex)
What is the mechanism of action of Daratumumab?
Several mechanisms:
Myeloma cells express CD-38; dara targets the CD-38 receptors.
Promotes T-cell activation
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity.
CD-38 is also expressed on surface of RBCs. So type and screen should be obtained before starting the treatment because daratumumab can interfere with the indirect Coombs test!
What are the benefits of using subcutaneous daratumumab vs. intravenous?
IV has higher transfusion reaction risk
IV Infusion times are prolonged (could take 8-10 hrs)
Subcutaneous administration does not require test dose
Less infusion related reactions with subcutaneous dosing.
It takes about 5 minutes to administer the subcutaneous dose, which is 15ml in volume.
What are the side effects of Daratumumab?
Upper respiratory tract infections:
Make sure patients are up-to-date on vaccines including flu, COVID, pneumonia
Revaccinate all post-transplant patients
If using Dara in relapse settings, then IVIG can be given in cases of low IgG titer (<100) and recurrent infections
CyBorD
What is “CyBorD”?
A triplet regimen consisting of cyclophophadmide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone.
Consider using in patients who have significant renal dysfunction
In this regimen, should bortezomib be weekly or biweekly in CyBorD?
Biweekly Velcade is given if the patient can tolerate, to achieve rapid disease control, so that myeloma induced kidney damage can be reversed.
Is it ever reasonable to transition to one of the lines of therapy discussed above, such as VRD if someone is started on CyBorD?
Lenolidomide is not nephrotoxic, but it is cleared renally!
So If patient has impaired renal function, build up of drug can cause enhanced side effects especially cytopenias.
Once Creatinine Clearance is stabilized above 30 ml/min, lenolidomide can be started.
Second generation drugs
Carfilzomib (Kyprolis)
What are side effects to counsel patients on regarding this drug?
Cardiotoxicity (ranging from hypertention to heart failure)
Baseline echo is recommended, but techincally not required
Infusion reactions
Thrombocytopenia
Neuropathy is usually not a concern with Carfilzomib!
Dose adjustments suggested if renal dysfunction while on therapy.
Pomalidomide (Pomalyst)
What are common side effects to counsel patients on regarding this drug?
Fatigue
Myelosuppression
Diarrhea
Dose adjustments required for dialysis
When do we use anti-microbial prophylaxis?
HSV: If they are on proteasome inhibitor or monoclonal antibody
PJP: She extrapolates NCCN guidelines and prescribes if on a regimen of >20mg dex weekly; also in patients on bi-specific antibodies and after CAR-T
About our guest
Kathyrn Maples, PharmD, BCOP is a clinical pharmacy specialist at The Winship Cancer Institute at Emory Healthcare in Atlanta, GA specializing in multiple myeloma. She received her PharmD from University of Georgia and completed her training at Virginia Commonwealth University Health System. She then spent some time at Memorial Sloan Kettering before returning to Georgia. Thank you SO MUCH for joining us!
The crew behind the magic:
Show outline: Vivek Patel
Production and hosts: Ronak Mistry, Vivek Patel, Dan Hausrath
Editing: Ronak Mistry, Vivek Patel
Shownotes: Maria Khan, Ronak Mistry
Graphics, social media management: Ronak Mistry